10 Best Database Management Systems Shortlist
Here's my pick of the 10 best software from the 25 tools reviewed.
Our one-on-one guidance will help you find the perfect fit.
Your team depends on reliable, efficient access to data. Whether you're managing high-traffic applications, scaling infrastructure, or ensuring security compliance, the right database management software helps keep everything running smoothly. But with so many options, choosing the best fit can be time-consuming.
I independently test and review software, focusing on what truly matters to CTOs. In this guide, I’ve evaluated the best database management solutions on the market. You’ll find insights on features, trade-offs, pricing, and how each tool fits different use cases.
Whether you need to optimize performance, simplify administration, or support complex workloads, this list will help you make the right choice for your team.
Why Trust Our Software Reviews
We’ve been testing and reviewing database management software since 2023. As IT and data specialists ourselves, we know how critical and difficult it is to make the right decision when selecting software.
We invest in deep research to help our audience make better software purchasing decisions. We’ve tested more than 2,000 tools for different IT use cases and written over 1,000 comprehensive software reviews. Learn how we stay transparent & our review methodology.
Best Database Management Systems Summary
| Tool | Best For | Trial Info | Price | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Best for multi-database environment monitoring | Free trial + demo available | Pricing upon request | Website | |
| 2 | Best for proactive performance monitoring | 30-day free trial + demo available | From $395/year (billed annually) | Website | |
| 3 | Best for query building with visual tools | Free trial + demo available | Pricing upon request | Website | |
| 4 | Best for companies in highly regulated industries | Free demo available | Pricing upon request | Website | |
| 5 | Best for MongoDB | Free plan available | From $19/user/month | Website | |
| 6 | Best data visualization features | 30-day free trial | From $125/user/month (billed annually) | Website | |
| 7 | Best SQL IDE | Free plan available | From $22.90/user/month | Website | |
| 8 | Best diagnostic features | 14-day free trial | From $1,275 (billed annually) | Website | |
| 9 | Best availability | Free plan available | Pricing upon request | Website | |
| 10 | Best security features | Free trial + demo available | Pricing upon request | Website |
-

Docker
Visit WebsiteThis is an aggregated rating for this tool including ratings from Crozdesk users and ratings from other sites.4.6 -

Pulumi
Visit WebsiteThis is an aggregated rating for this tool including ratings from Crozdesk users and ratings from other sites.4.8 -

GitHub Actions
Visit Website
Best Database Management Systems Reviews
Below are my favorite database management systems, including details on why I chose them, pricing information, and a later section on what I assessed when making my list:
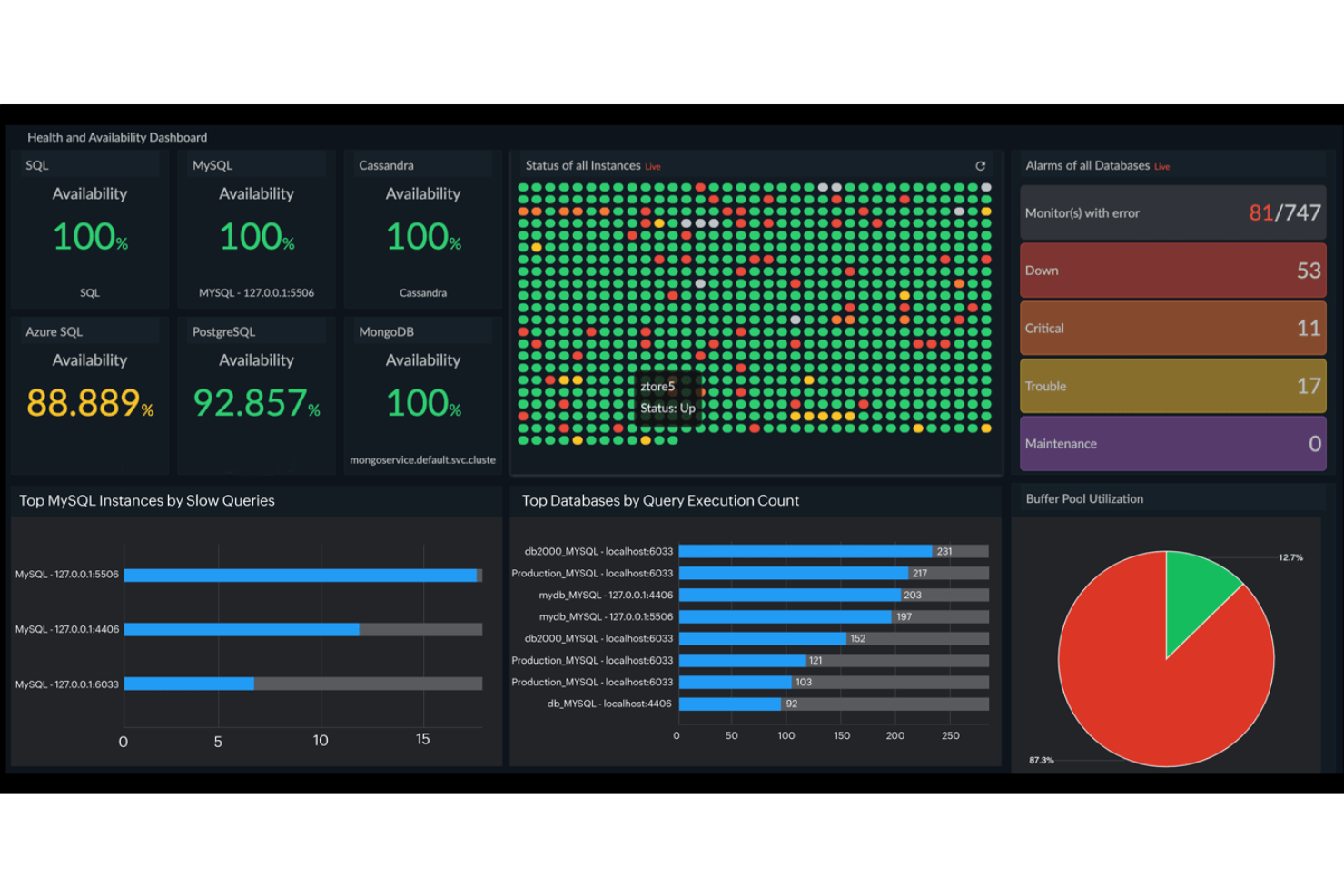
Site24x7 is a cloud-based monitoring platform designed to help IT teams oversee the performance and availability of their infrastructure. It offers tools to monitor servers, networks, applications, and databases, providing insights into system health and performance.
Why I picked Site24x7: I picked Site24x7 because it supports monitoring for a wide variety of databases, including SQL, NoSQL, and cloud-based systems like Microsoft SQL Server, MySQL, MongoDB, and Amazon RDS. It gives your team detailed visibility into database performance through metrics like query execution time, throughput, and error rates. These insights help you identify slow queries and keep performance on track.
Site24x7 Standout Features and Integrations:
Features include the ability to monitor database health and availability through auto-discovered metrics, offering a comprehensive view of system status. Site24x7 also allows for the monitoring of hybrid environments, enabling visibility across both on-premises and cloud-based databases. Additionally, it provides tools to analyze and troubleshoot query attributes.
Integrations include AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, VMware, Amazon EventBridge, Zoho Analytics, Moogsoft, Jira, ConnectWise, PagerDuty, Microsoft Teams, and Slack.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Offers real-time alerts across various channels
- Customizable dashboards and reports
- Comprehensive monitoring for various systems
Cons:
- Lacks database management tools beyond monitoring
- Excessive alerts can be overwhelming for users
New Product Updates from Site24x7
UK Data Center Launch by Site24x7
Site24x7 has launched a UK data center, enabling users to migrate workloads for better connectivity, lower latency, and data residency compliance. More details are available at Site24x7.
Best for proactive performance monitoring
ManageEngine Applications Manager is an IT infrastructure and application monitoring tool that provides deep visibility into application performance, server health, and database operations across on-premises, cloud, and hybrid environments.
Why I picked ManageEngine Applications Manager: I picked this platform because of its robust end-to-end monitoring across multiple layers of the IT stack. It stood out during my evaluation for its AI-powered anomaly detection, real user and synthetic transaction monitoring, and the ability to monitor databases, cloud services, servers, and applications in one place. These capabilities are especially valuable for IT teams managing complex environments that demand proactive performance oversight.
ManageEngine Applications Manager Standout Features and Integrations:
Features include code-level diagnostics for Java, .NET, and Node.js apps, customizable dashboards, automated discovery and dependency mapping, and in-depth monitoring of databases such as Oracle, MySQL, SQL Server, MongoDB, and PostgreSQL. The platform also supports real user monitoring (RUM), synthetic testing, and AI-driven alerting for faster issue resolution.
Integrations include databases like Oracle, MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, AWS Aurora, and Azure SQL. It also offers out-of-the-box integration with Slack, ServiceNow, and Site24x7.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Covers monitoring of microservices like Docker, Kubernetes
- In-built reporting tools
- Allows alert configuration at different levels
Cons:
- Initial setup and configuration can be complex
- Outdated, clunky user interface
New Product Updates from ManageEngine Applications Manager
ManageEngine Applications Manager Integrates PAM360
ManageEngine Applications Manager now supports PAM360 integration, enabling automatic password synchronization for server-monitored resources, enhancing privileged access management. For more details, refer to the ManageEngine Release Notes.
dbForge Studio for MySQL is a comprehensive GUI tool designed to facilitate MySQL and MariaDB database development, management, and administration.
Why I picked dbForge Studio for MySQL: The platform’s advanced code completion and syntax highlighting make writing SQL code easier, while its visual query builder allows even novice users to construct complex queries without deep SQL knowledge. In addition, the software offers tools for schema and data synchronization, ensuring consistency across databases.
dbForge Studio for MySQL Standout Features and Integrations:
Features include the data comparison tool for you to quickly compare and synchronize database content, helping maintain consistency across environments. The backup and restore feature ensures that data can be securely backed up and easily restored, while the integration with version control systems lets you track changes and roll back to previous versions of database schemas and data.
Integrations include Git, SVN, Mercurial, SourceGear Vault, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, Amazon RDS, MariaDB, and Oracle Cloud.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Allows secure connections via SSH
- Built-in tools to optimize and monitor database performance
- Tools for comparing and synchronizing data
Cons:
- May be complex for beginners
- Interface is a bit cluttered
OneTrust is a risk management solutions platform that provides automation services for areas such as data privacy, discovery, and ethics.
Why I picked OneTrust: OneTrust provides dedicated compliance management tools for various regulatory standards from all over the world. During my evaluations, I tested and was satisfied with the management tools for HIPAA, GDPR, SOC 2, SOX, and PCI DSS. For companies in industries that are heavily regulated, like finance and healthcare, this feature makes it easy to comply and avoid penalties when you get audited.
OneTrust Standout Features and Integrations:
Features that made regulatory compliance with the OneTrust Platform more manageable, in my opinion, include the Privacy and Data Management Cloud. It provides built-in tools for data discovery and governance, consent and preference management, and privacy management to help you create a more secure and confidence-inspiring user experience.
I also tested the ESG and Sustainability Cloud, where I found you can track the metrics that usually go into transparency and sustainability reports in one place. From here, you can also generate reports and carry out analytical functions with full automation capabilities.
Integrations are pre-built for Kafka, Amazon S3, Apache Cassandra, Box, Mailchimp, HubSpot, ServiceNow, Snowflake, Jira, and Bitbucket.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Large integration library
- Strong privacy and data protection features
- Robust compliance management features
Cons:
- Relatively steep learning curve
- Extensive initial setup
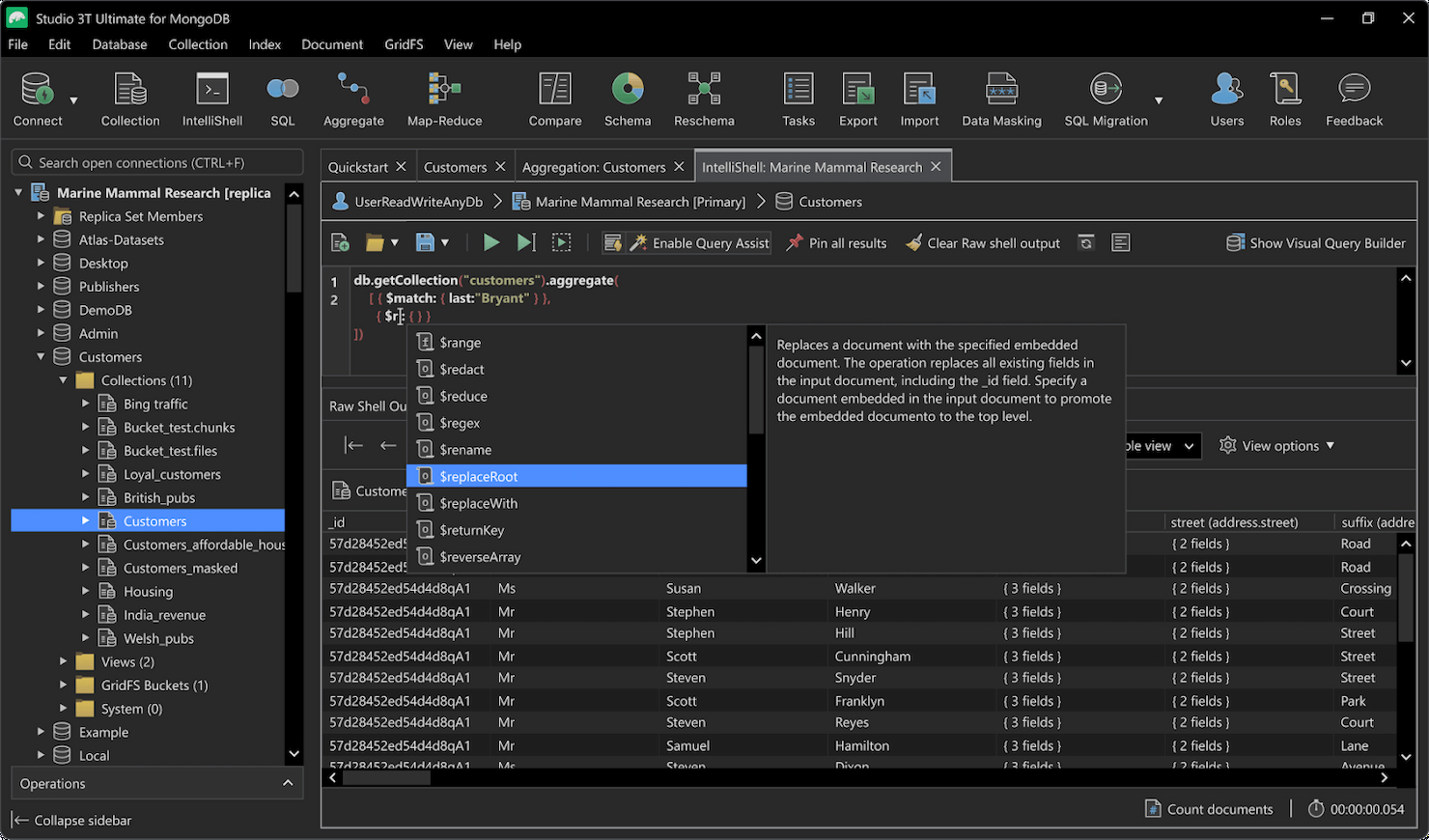
Studio 3T is a collection of tools for working with MongoDB that provides an IDE, GUI, and client both on and off Atlas.
Why I picked Studio 3T: I really liked the Visual Query Builder in Studio 3T, which allowed me to construct MongoDB queries with a drag-and-drop interface alongside tree and table views. Because I didn’t have to write out the code myself, I was able to move faster, and I believe this is also a key feature for people that are still new to MongoDB.
Studio 3T Standout Features and Integrations:
Features that made working with MongoDB easy in Studio 3T include IntelliShell, which provides Mongo-specific code editing features such as completion and error highlighting. I could also import SQL databases and tables from various sources, including MySQL, Oracle, IBM Db2, and Microsoft SQL Server, into one MongoDB collection, complete with relationship mapping.
Integrations are pre-built for Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle, IBM Db2, and Oracle.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Visual query and aggregation builder
- SQL to MongoDB and vice versa
- Robst MongoDB management and editing features
Cons:
- Relatively underpowered free version
- Costs more than similar alternatives
Spotfire is a scalable and fully governed BI and data analytics platform from TIBCO, a company that provides solutions for cloud integration as well as data management, virtualization, and analytics.
Why I picked TIBCO Spotfire: I enjoyed analytics with Spotfire because it uses TIBCO’s hyperconverged analytics feature to provide more detailed visualizations for both prescriptive and predictive analysis. The visualizations were fully responsive across both real-time and historical data, allowing me to derive more insights from them.
TIBCO Spotfire Standout Features and Integrations:
Features that made me recommend Spotfire for data visualization and analytics include the ability to create custom apps using the Spotfire Mods tool, complete with an API, workflow management, and visualization library.
The platform also provides in-depth geoanalytics functionality that allows you to analyze multi-layered maps with contextualized location data. Spotfire actually recognized GPS data in my test dataset and accurately overlaid it onto an interactive map.
Integrations are pre-built for Docker, Google Cloud, Azure, AWS, Maven, Spring Cloud Config, SAP, OpenShift, Cloud Foundry, and Salesforce.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Location-based analytics
- Interactive data visualization for analytics
- Allows you to build custom apps
Cons:
- Spotty documentation
- Smaller data visualization library compared to dedicated analytics too
DataGrip is a SQL database management integrated development environment (IDE) from JetBrains.
Why I picked DataGrip: During my evaluation, I found DataGrip excelled as much as any IDE could, and I’d recommend it to anyone that regularly works with SQL code. It provides advanced code editing features such as completion, error highlighting, inspections, and refactoring.
DataGrip Standout Features and Integrations:
Features I liked while editing SQL code in DataGrip include the ability to compare database schema and see all their differences so I could generate more effective migration scripts whenever I needed them.
I also got a lot of use out of the run and debug configurations which allowed me to set various permanent and temporary parameters for executing scripts. This way, I could create ideal environments without having to set them up every time I wanted to run a script.
Integrations are pre-built for Snowflake, Azure Databricks, GitHub, GitLab, Docker, and ClickHouse.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Supports major database systems
- Advanced SQL editing features
- Supports pre-execution configurations for scripts
Cons:
- Resource intensive
- Requires extensive knowledge of SQL
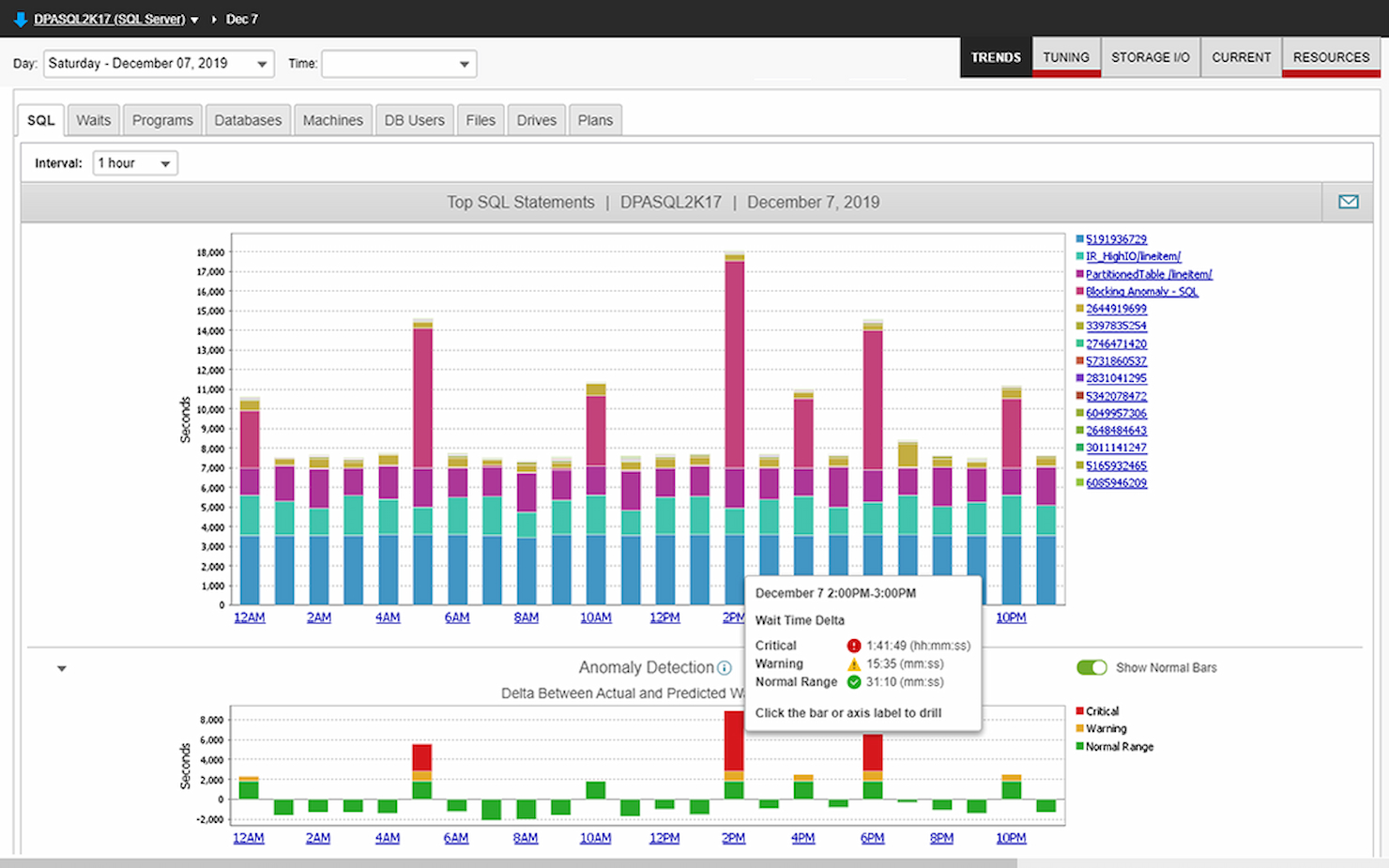
SolarWinds Database Performance Analyzer (DPA) is a DBMS tool for monitoring and optimization on both cloud and on-premise environments.
Why I picked SolarWinds Database Performance Analyzer: SolarWinds DPA’s database optimization features made it easy to identify and resolve issues that impacted system performance. It could sniff out existing bottlenecks along with their causes and potential fixes, as well as applications displaying signs of regression so I could address them before they had a significant negative impact on the rest of the system.
SolarWinds Database Performance Analyzer Standout Features and Integrations:
Features I liked for managing issues with DPA include the anomaly detection tool that monitors your systems and alerts you of any unusual activity. You can also increase or decrease the sensitivity levels of the detector depending on perceived threat levels.
I could also tie resource provisioning to performance, ensuring I got the most out of my current hardware setup and avoided unnecessary upgrades.
Integrations are pre-built for IBM Db2, PostgreSQL, MySQL, Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, Amazon Aurora, SAP ASE, MariaDB, and Azure SQL Database.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Decent resource management features
- Robust diagnostic tools
- Anomaly detector
Cons:
- Limited free trial
- Costly licensing model
Neptune is a fully managed graph database from Amazon that can store billions of relationships for building and running graph applications in the cloud.
Why I picked AWS Neptune: Neptune caught my attention with its comprehensive approach to ensuring availability, which reflects what I’ve come to expect from AWS. Most notably, it splits databases into chunks of 10GB each and replicates them across three availability zones six ways.
AWS Neptune Standout Features and Integrations:
Features I liked in Neptune include the fault-tolerant storage that was capable of managing the loss of up to two and three copies of data without affecting the database’s read and write availability, respectively. It also increases system availability with self-healing functions where it automatically scans disks and data blocks for errors and finds replacements from healthy copies.
Integrations are native for other AWS products and services, including S3, Lambda, SageMaker, Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), Key Management Service (KMS), CloudFormation, and Kinesis.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Databases are durable
- Native AWS integrations
- High availability
Cons:
- Limited to AWS
- Complex pricing structure
IBM Db2 is a cloud-native solution for real-time analytics and low latency with a focus on availability, security, and resiliency.
Why I picked IBM Db2: Db2’s auditing features made it easy for me to stay on top of data access to protect my databases from unknown threats. I was able to declare events I wanted flagged and have Db2 create audit trails, then provide me with detailed logs that I could review to pinpoint suspicious activity.
IBM Db2 Standout Features and Integrations:
Features that made me recommend Db2 for security-conscious environments include the db2cluster command, which gave me access to my clusters as a manager and shared file system. I used it to implement role-based access control (RBAC) across my databases with administrators at the top. I also liked row and column access control (RCAC), which I used to manage user access by individual rows and columns depending on what they needed.
Integrations are available with Red Hat OpenShift, AWS, Kubernetes, and Azure.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- High availability
- Supports advanced querying
- Robust security features
Cons:
- Slow performance at times
- Limited public cloud support
Other Database Management System To Consider
Below are some DBMS tools that I evaluated and still liked, even though they didn’t make the main list:
- Redis
Caching functionality
- Snowflake
Multi-cloud management functionality
- Apache Cassandra
Open-source option
- ClickHouse
Online analytical processing features
- Syniti
Data replication features
- dbForge Edge
For unified database management
- DbVisualizer
Database testing features
- PostgreSQL
Relational database management system
- MySQL
Local transaction support
- Valentina
For MariaDB
- Oracle Enterprise Manager
For Oracle Database
- PopSQL
For data analysis collaboration
- Sadas Engine
For columnar databases
- RazorSQL
Database browser
- Microsoft SQL Server
For Azure-hosted databases
Related Software Reviews
If you still haven't found what you're looking for here, check out these alternative tools that we've tested and evaluated.
- Network Monitoring Software
- Server Monitoring Software
- SD-Wan Solutions
- Infrastructure Monitoring Tools
- Packet Sniffer
- Application Monitoring Tools
Database Management Software Selection Criteria
When selecting the best database management software to include in this list, I considered common buyer needs and pain points like scalability for growing data volumes and ease of integration with existing infrastructure. I also used the following framework to keep my evaluation structured and fair:
Core Functionality (25% of total score)
To be considered for inclusion in this list, each solution had to fulfill these common use cases:
- Store and retrieve structured data
- Support SQL queries and indexing
- Provide backup and recovery options
- Offer access control and security settings
- Scale across multiple users and workloads
Additional Standout Features (25% of total score)
To help further narrow down the competition, I also looked for unique features, such as:
- Support for multi-cloud and hybrid environments
- Advanced AI-powered query optimization
- Automated schema management and migration tools
- Built-in analytics and reporting capabilities
- Native integrations with third-party applications
Usability (10% of total score)
To get a sense of the usability of each system, I considered the following:
- Intuitive user interface and dashboard layout
- Ease of database setup and configuration
- Availability of low-code or no-code management options
- Clarity of documentation and in-app guidance
- Mobile or web-based access for administrators
Onboarding (10% of total score)
To evaluate the onboarding experience for each platform, I considered the following:
- Availability of guided setup wizards and tutorials
- Access to pre-built database templates
- Quality and depth of training videos and webinars
- Interactive product tours and documentation
- Support for seamless data migration from existing systems
Customer Support (10% of total score)
To assess each software provider’s customer support services, I considered the following:
- Availability of 24/7 live support or chat assistance
- Responsiveness of email and ticketing systems
- Access to a knowledge base and troubleshooting guides
- Community forums and user discussion groups
- Dedicated account managers for enterprise customers
Value For Money (10% of total score)
To evaluate the value for money of each platform, I considered the following:
- Pricing transparency and availability of free trials
- Flexibility of pricing tiers based on usage needs
- Cost-effectiveness compared to competitors with similar features
- Inclusion of core features without requiring expensive add-ons
- Licensing models that suit both small businesses and large enterprises
Customer Reviews (10% of total score)
To get a sense of overall customer satisfaction, I considered the following when reading customer reviews:
- Quality of customer support based on real user experiences
- Consistency of positive feedback across multiple platforms
- Common pain points mentioned by users
- Reliability and stability of the software in long-term use
- Ease of use for both technical and non-technical users
How To Choose Database Management Software
It’s easy to get bogged down in long feature lists and complex pricing structures. To help you stay focused as you work through your unique software selection process, here’s a checklist of factors to keep in mind:
| Factor | What to Consider |
| Scalability | Will the software handle your current and future data needs? Look for options that support large datasets, high transaction volumes, and distributed architectures. |
| Integrations | Does it integrate with your existing tech stack? Ensure compatibility with key applications like BI tools, cloud storage, and workflow automation systems. |
| Customizability | Can you configure it to fit your team’s needs? Look for flexible data structures, user roles, and workflow automation options. |
| Ease of Use | How intuitive is the interface? Your team should be able to navigate and manage databases efficiently without steep learning curves. |
| Budget | Does the pricing align with your company’s budget? Check for transparent pricing models, free trials, and hidden costs related to storage, users, or advanced features. |
| Security Safeguards | Are strong security measures in place? Look for encryption, access controls, compliance certifications, and audit logs to protect sensitive data. |
Trends in Database Management Software
In my research, I sourced countless product updates, press releases, and release logs from different database management software vendors. Here are some of the emerging trends I’m keeping an eye on:
- AI-Driven Query Optimization: More databases are using AI to automatically improve query performance and reduce latency. Vendors like Oracle and Google Cloud are integrating machine learning to predict query patterns and optimize indexing without manual intervention.
- Serverless Databases: Managed, pay-as-you-go NoSQL databases are gaining popularity, eliminating the need for provisioning and maintenance. AWS Aurora Serverless and Google Firestore let teams scale storage and compute dynamically based on workload demands.
- Multi-Model Databases: Businesses want flexibility in handling structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data in a single system. Vendors like ArangoDB and Couchbase are blending SQL, graph, key-value, and document storage to support diverse use cases.
- Zero Trust Security Models: Traditional perimeter-based security is becoming outdated, and database vendors are moving toward stricter identity-based access controls. Features like just-in-time authentication, attribute-based access control, and granular data masking are becoming standard.
- Edge Computing and Distributed Databases: With more businesses processing data closer to users, databases that support distributed and edge deployments are in demand. CockroachDB and FaunaDB are leading the way with architectures designed for high availability across multiple regions.
What Is Database Management Software?
Database management software is a tool that helps organizations store, organize, retrieve, and secure their data efficiently. IT teams, database administrators, and developers use these tools alongside specialized database DevOps tools to manage large datasets, ensure data consistency, and support business operations. Features like query optimization, automated backups, and access controls help with performance, security, and reliability. These tools make it easier to handle growing data needs while reducing manual work and minimizing errors.
Features of Database Management Software
When selecting database management software, keep an eye out for the following key features:
- Query optimization: Improves the efficiency of database queries to speed up response times and reduce server load.
- Automated backups: Ensures data is regularly saved and recoverable in case of accidental deletion or system failures.
- Access control: Manages user permissions to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access.
- Multi-model support: Allows the database to store and process different data types like relational, document, and graph formats.
- Replication and failover: Duplicates data across multiple locations to enhance availability and prevent downtime.
- Data indexing: Organizes data in a way that makes retrieval faster and more efficient for queries.
- Scalability options: Enables databases to grow with increasing data volumes and user demands without performance issues.
- Logging and auditing: Tracks database activity for security, compliance, and troubleshooting purposes.
- Encryption: Protects data at rest and in transit to prevent unauthorized access and breaches.
- Integration capabilities: Connects with other business tools, cloud platforms, and analytics software for a unified workflow.
Benefits of Database Management Software
Implementing database management software provides several benefits for your team and your business. Here are a few you can look forward to:
- Better data organization: Helps structure and store data efficiently, making it easier to find and manage information.
- Faster query performance: Optimizes search and retrieval processes, reducing wait times for data-heavy applications.
- Stronger security controls: Provides access restrictions, encryption, and audit logs to protect sensitive information.
- Easier scalability: Adapts to growing data volumes and user demands without major disruptions.
- Improved reliability: Reduces the risk of data loss with automated backups, failover options, and redundancy features.
- Simplified data sharing: Enables teams to access and collaborate on data across different locations and departments.
- Lower maintenance effort: Automates routine database tasks like indexing, backup scheduling, and performance tuning.
Costs and Pricing of Database Management Software
Selecting database management software requires an understanding of the various pricing models and plans available. Costs vary based on features, team size, add-ons, and more. The table below summarizes common plans, their average prices, and typical features included in database management software solutions:
Plan Comparison Table for Database Management Software
| Plan Type | Average Price | Common Features |
| Free Plan | $0 | Basic data storage, limited queries, single-user access, and community support. |
| Personal Plan | $10-$30/user/month | Increased storage, faster query processing, multi-device access, and basic security controls. |
| Business Plan | $40-$100/user/month | Advanced security features, role-based access control, automated backups, and API integrations. |
| Enterprise Plan | Custom pricing | Custom scalability, dedicated support, compliance certifications, and AI-driven performance optimization. |
Database Management Software FAQs
Here are some answers to common questions about database management software:
How do I choose the right database management software for my business?
Selecting the right database management software depends on your specific needs. Consider factors like the type of data you're handling, scalability requirements, budget constraints, and integration capabilities with your existing systems. It's essential to evaluate each option's features and choose one that aligns with your business objectives.
What are the differences between SQL and NoSQL databases?
SQL databases are relational, using structured query language for defining and manipulating data, and are ideal for structured data with predefined schemas. NoSQL databases are non-relational, supporting a variety of data models like document, key-value, graph, or wide-column, and are suitable for unstructured or semi-structured data, offering flexibility and scalability.
Can I migrate my existing data to a new database management system?
Yes, migrating data to a new database management system is possible but requires careful planning. You'll need to map existing data structures to the new system, ensure data integrity during the transfer, and possibly transform data formats. It's advisable to back up your data and test the migration process thoroughly before full implementation.
How does database management software handle data security?
Database management software employs various security measures to protect data, including user authentication, access controls, encryption, and regular audits. Implementing these features helps prevent unauthorized access and ensures compliance with data protection regulations.
What is the role of a database administrator in managing database software?
A database administrator (DBA) is responsible for installing, configuring, and maintaining the database management system. Their duties include ensuring data integrity, implementing security measures, performing backups, optimizing performance, and troubleshooting any issues that arise.
How do cloud-based database management systems compare to on-premises solutions?
Cloud-based database management systems offer benefits like scalability, reduced hardware costs, and accessibility from anywhere with an internet connection. On-premises solutions provide greater control over data and may be preferred for sensitive information requiring strict compliance. The choice depends on your organization's specific needs and resources.
What Next?
After you’ve chosen the ideal database management solution for your needs, you’ll need to know how to get the most out of it. Aside from the integrations I mentioned in this article, you can get more from the tool by using it in conjunction with other types of technical software and implementing proven best practices across all your workflows.
Make sure you subscribe to our newsletter to get more insights into how you can do exactly this.