Best NoSQL Databases Shortlist
Below is my recommended list of NoSQL databases, along with a summary of what they do best:
Our one-on-one guidance will help you find the perfect fit.
Choosing the proper NoSQL database can streamline data management, scalability, and performance while boosting flexibility and efficiency—whether you're handling large-scale web applications, real-time analytics, or IoT data processing. However, the sheer number of available NoSQL database solutions—combined with the challenge of navigating different data models, scaling complexities, and integration concerns—can make selecting the best option overwhelming.
In this article, I leverage my years of experience in database management and testing dozens of NoSQL solutions to break down what these databases offer, who they’re best suited for, and how they can help you optimize performance, improve data accessibility, and scale seamlessly.
Why Trust Our NoSQL Database Reviews
We’ve been testing and reviewing NoSQL databases since 2023. As developers ourselves, we know how critical and difficult it is to make the right decision when selecting software. We invest in deep research to help our audience make better software purchasing decisions.
We’ve tested more than 2,000 tools for different data management use cases and written over 1,000 comprehensive software reviews. Learn how we stay transparent & our hybrid cloud solution review methodology.
Best NoSQL Databases Summary
| Tool | Best For | Trial Info | Price | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Best serverless NoSQL database | Free tier available | From $1/month | Website | |
| 2 | Best NoSQL database for fully-functional ACID transactions | Free versions available | From $789/core/year | Website | |
| 3 | Best wide-column NoSQL database | Free version available | No paid plan | Website | |
| 4 | Best multi-model NoSQL database | Free version available | Enterprise edition from $5,970 | Website | |
| 5 | Best search-based document database | Free trial available | From $95/month | Website | |
| 6 | Best column-oriented database for storing very large datasets | Free version available | No paid option | Website | |
| 7 | Best graph-based NoSQL database | Free version available | Pricing upon request | Website | |
| 8 | Best cloud- and grid-based NoSQL database | Free version available | Fixed license from $15,456/year | Website | |
| 9 | Best NoSQL database for user-friendliness | Free version available | From $1.25/million requests; read operations from $0.25/million requests | Website | |
| 10 | Best for SQL-like functionality | Free trial available | From $0.28/hr per node | Website | |
| 11 | Best document-based NoSQL database | Free version available | From $57/month or serverless from $0.10/million reads | Website | |
| 12 | Best key-value NoSQL database | Free version available | From $7/month or $0.881/hour | Website |
-

Docker
Visit WebsiteThis is an aggregated rating for this tool including ratings from Crozdesk users and ratings from other sites.4.6 -

Pulumi
Visit WebsiteThis is an aggregated rating for this tool including ratings from Crozdesk users and ratings from other sites.4.8 -

GitHub Actions
Visit Website
Best NoSQL Database Reviews
Here are my recommendations of the 12 best NoSQL databases and the scenarios where I think each one performs best.
IBM Cloud is a fully managed, distributed database that runs on a serverless schematic, meaning you don’t have to manage server configuration and scaling. This lets you build and run databases without worrying about the backend.
Why I Picked IBM Cloudant: I picked IBM Cloudant because it’s incredibly secure. You only pay for the resources you use, and you can scale up or down as your data needs change. For security, I was impressed by IBM Key Protect, which gave me total control and visibility over encrypted keys.
IBM Cloudant Standout Features and Integrations:
Features include its multi-region replication, high availability, and automatic failover for globally distributed applications. It also offers integrated full-text search powered by Apache Lucene, making it easier to query and analyze large datasets efficiently. Additionally, Cloudant provides offline-first synchronization, allowing mobile and web applications to function seamlessly even with intermittent connectivity.
Integrations include IBM App Connect, IBM Cloud Log Analysis, IBM Watson, Apache Spark, IBM Cloud Functions, Apache CouchDB, Tableau, and IBM Cognos Analytics.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Free version available
- Serverless schema for easy configuration
- Comprehensive security
Cons:
- Slow time to index large databases
- Some documentation is out of date
RavenDB is a multi-document database that supports ACID (Atomic, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability) transactions. This helps prevent data from accidentally falling into an inconsistent state. The platform is used by nationally recognized companies such as Toyota, Verizon, and Medicaid.
Why I Picked RavenDB: Aside from the visually appealing interface, I like that RavenDB supports ACID transactions. This ensures transactions can only change data in predictable ways and that those changes are always saved, even during a system crash.
RavenDB Standout Features and Integrations:
Features include built-in full-text search, allowing fast and efficient querying of unstructured data without needing an external search engine. It also offers automatic indexing, reducing the need for manual query optimization and improving performance over time. Additionally, RavenDB supports multi-master replication, ensuring high availability and real-time synchronization across distributed environments.
Integrations include FastReport, Elasticsearch, Grafana, Power BI, Node.js, .NET, Python, and Kubernetes.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- On-premise and cloud versions
- ACID transactions ensure greater data consistency and time-saving
- Easy-to-use interface
Cons:
- Lacking community support and documentation
- Enterprise version is expensive
Apache Cassandra is an open-source, wide-column database supporting hybrid cloud and on-premises replicating and audit logging. Because the platform is freely available and used by thousands of companies, I think it is an excellent solution for businesses that want to manage extensive active data sets at low cost.
Why I Picked Apache Cassandra: Cassandra stands out as a powerful wide-column database with lots of scalability. You can add more servers horizontally to the cluster as your data needs increase. Also, Cassandra uses a column-family data model, so it’s accessible to traditional relational database users.
Cassandra Standout Features and Integrations:
Features include a masterless architecture, ensuring no single point of failure and enabling continuous availability even during node failures. It also offers lightweight transactions (LWT) using Paxos, providing strong consistency when needed without sacrificing performance. Additionally, Cassandra handles write-heavy workloads, making it an ideal choice for applications requiring high-speed data ingestion at scale.
Integrations include New Relic, IRI Voracity, DbVisualizer, Sematext Cloud, Flex83, Retool, and DbSchema.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Horizontal scaling to accommodate growing data needs
- Can handle large volumes of unstructured data
- Support for hybrid cloud (private and public) and on-premises
Cons:
- Requires periodic manual maintenance
- No ad-hoc queries
OrientDB is an open-source, multi-model database. It supports all types of NoSQL databases, including graph, key-value, object, and document models. So your business can build and manage multiple NoSQL databases on one system without investing in various products.
Why I Picked OrientDB: I chose OrientDB because its engine is built from the ground up to support the full functionality of each NoSQL database type natively. I found this to be a better approach than merely replicating the interfaces of other models, which achieves limited speed and scalability.
OrientDB Standout Features and Integrations:
Features include its multi-model architecture, which natively supports graph, document, object, and key/value data models within a single database engine. It also offers ACID compliance, ensuring strong consistency and reliability across transactions, which is uncommon among many NoSQL databases. Additionally, OrientDB features a distributed architecture with sharding and replication, enabling seamless horizontal scaling and high availability.
Integrations include Teleporter, Orient DBL, Spark Connector, and Neo4j Importer.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Free community edition is great for small businesses
- Easy to setup and use
- Native support Graph, Key-Value, Document, and Object databases
Cons:
- Small community and limited documentation
- High upfront cost for Enterprise edition
Elasticsearch is a distributed database that has a uniquely fast search function. Based on the Apache Lucene library, you can use Elasticsearch across various industries to improve the customer experience, streamline the DevOps lifecycle, and gain insights into production environments.
Why I Picked Elasticsearch: I chose Elasticsearch because it’s a powerhouse for searching data. Aside from storing and analyzing large amounts of data in real time, Elasticsearch can provide answers in milliseconds. It achieves this speed by converting unstructured data into specially configured documents optimized for language-based searches. This allows users to find the information they need quickly and easily.
Elasticsearch Standout Features and Integrations:
Features include its distributed search architecture, which enables high-speed querying and indexing across massive datasets. It also offers built-in support for full-text search with advanced features like fuzzy matching, autocomplete, and relevancy scoring to refine results. Additionally, Elasticsearch provides real-time analytics and visualization through its integration with Kibana, making it a suitable tool for monitoring, log analysis, and business intelligence.
Integrations include 1Password, Amazon CloudWatch, AWS ECS, Graphite, HA-Proxy, and LastPass.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Affordable basic plan
- Huge range of integrations
- Unique search capabilities
Cons:
- Lack of security features
- Concept can be confusing at first
HBase is a column-oriented, NoSQL database on the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS). The HBase platform is particularly good at managing extensive data, as the system is almost entirely fault-tolerant.
Why I Picked HBase: HBase stood out because it is extremely good with large datasets. It can scale across thousands of servers and accommodate data up to terabytes. I also appreciated that HBases uses HDFS to detect faults across all servers and automatically recover quickly. It excelled at minimizing server downtime for large systems.
HBase Standout Features and Integrations:
Features include deep integration with Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS), enabling efficient storage and processing of massive datasets across distributed clusters. It features automatic sharding, evenly distributing data and allowing for seamless horizontal scaling without manual intervention. Additionally, HBase supports real-time read and write access with strong consistency, making it ideal for applications that require low-latency performance on large-scale data.
Integrations include Hive, Apache Hadoop, Apache Spark, Apache Kafka, Apache Hive, Zookeeper, Flink, and Grafana.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Horizontally scalable across thousands of servers
- Integration with Apache Hadoop
- Free to use
Cons:
- CPU and memory intensive
- Fewer built-in features than Cassandra – relies on third-party integration
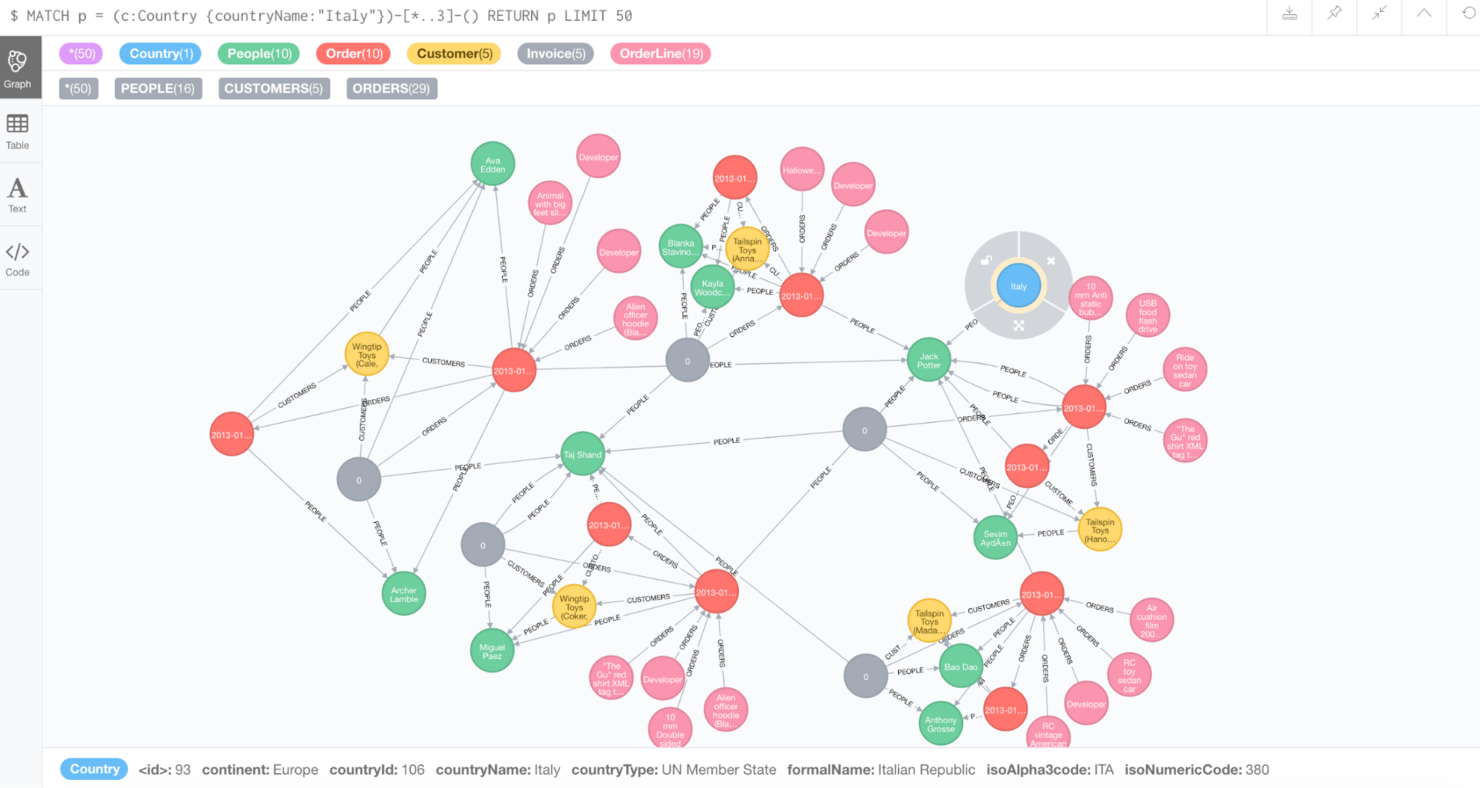
Neo4j is a graph-based NoSQL database used to develop applications, create and deploy Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) pipelines, and perform detailed analytics. It is particularly suited to data scientists, application developers, and similar enterprises. With the intuitive graph-based user interface, establishing patterns and relationships with large amounts of data is easy.
Why I Picked Neo4j: Neo4j grabbed my interest because of its clear user interface and advanced graphing capabilities. I found it was helpful for uncovering hidden insights in complex data relationships, where trends and patterns may not be obvious right away. I was also impressed by how easily the platform scales horizontally. This is thanks to Autonomous Clustering, which automatically copies your datasets to the most optimal servers based on your rules and guidelines.
Neo4j Standout Features and Integrations:
Features include its native graph database architecture, which enables highly efficient relationship queries that outperform traditional relational databases for connected data. It also features Cypher, a powerful graph query language designed for intuitive and complex relationship-based searches. Additionally, Neo4j offers advanced visualization tools that help users explore data connections and uncover insights without needing extensive SQL expertise.
Integrations include Apache Spark, Kafka Connect, and the Neo4j Data Warehouse connector.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Surprisingly easy to learn and use
- Strong community and documentation
- ACID transactions ensure database operations happen across all nodes
Cons:
- New versions can introduce new errors
- Custom pricing for Enterprise edition
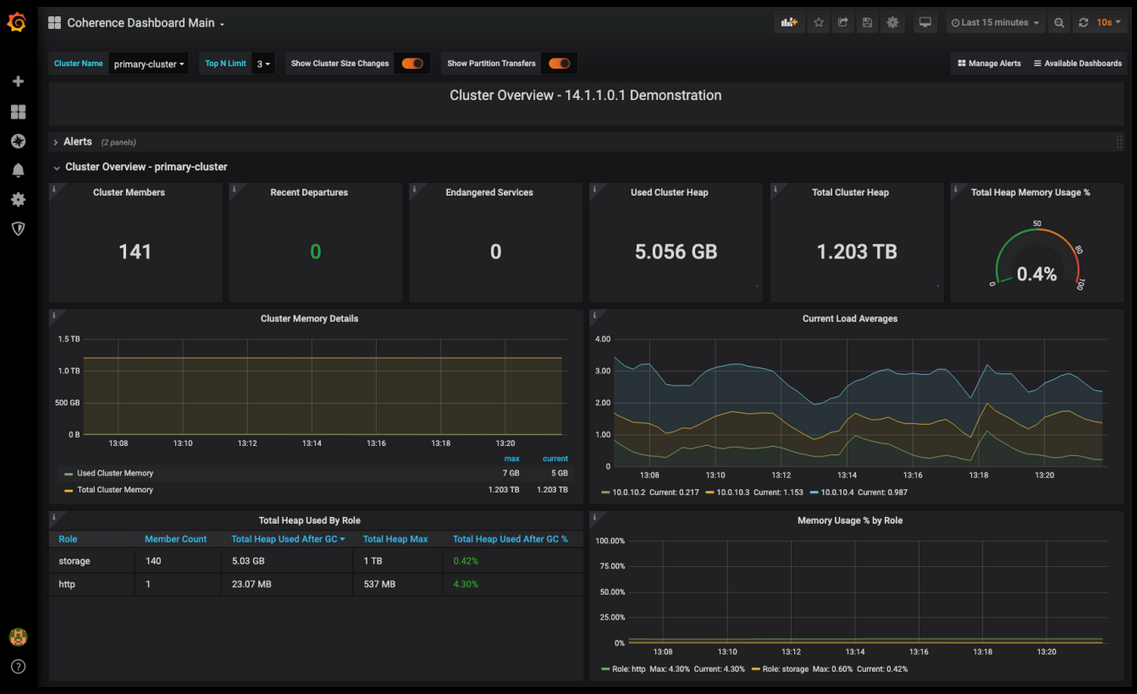
Oracle Coherence is an in-memory, key-value database that delivers strong scalability and performance for enterprise applications. Using low-latency data storage to read, write, and query latencies allows businesses — running multiple applications in different languages — to maintain data consistency in real-time quickly.
Why I Picked Oracle Coherence: What I love about Oracle Coherence is its support for asynchronous event streaming. This means you can incorporate event models into your event-driven architecture, allowing for efficient communication between microservices like servers and clients.
Oracle Coherence Standout Features and Integrations:
Features include real-time data grid capabilities, enabling ultra-fast in-memory data processing for high-performance applications. It also offers dynamic scaling, allowing clusters to expand and contract automatically based on workload demands. Additionally, Coherence supports federated caching, which ensures data consistency across multiple geographic regions by synchronizing caches in real-time.
Integrations include Spring, Oracle WebLogic Server, and Oracle NoSQL database.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Strong community support and documentation
- Many features to maintain data consistency
- Free to use
Cons:
- Difficult upgrade process
- Limited default security
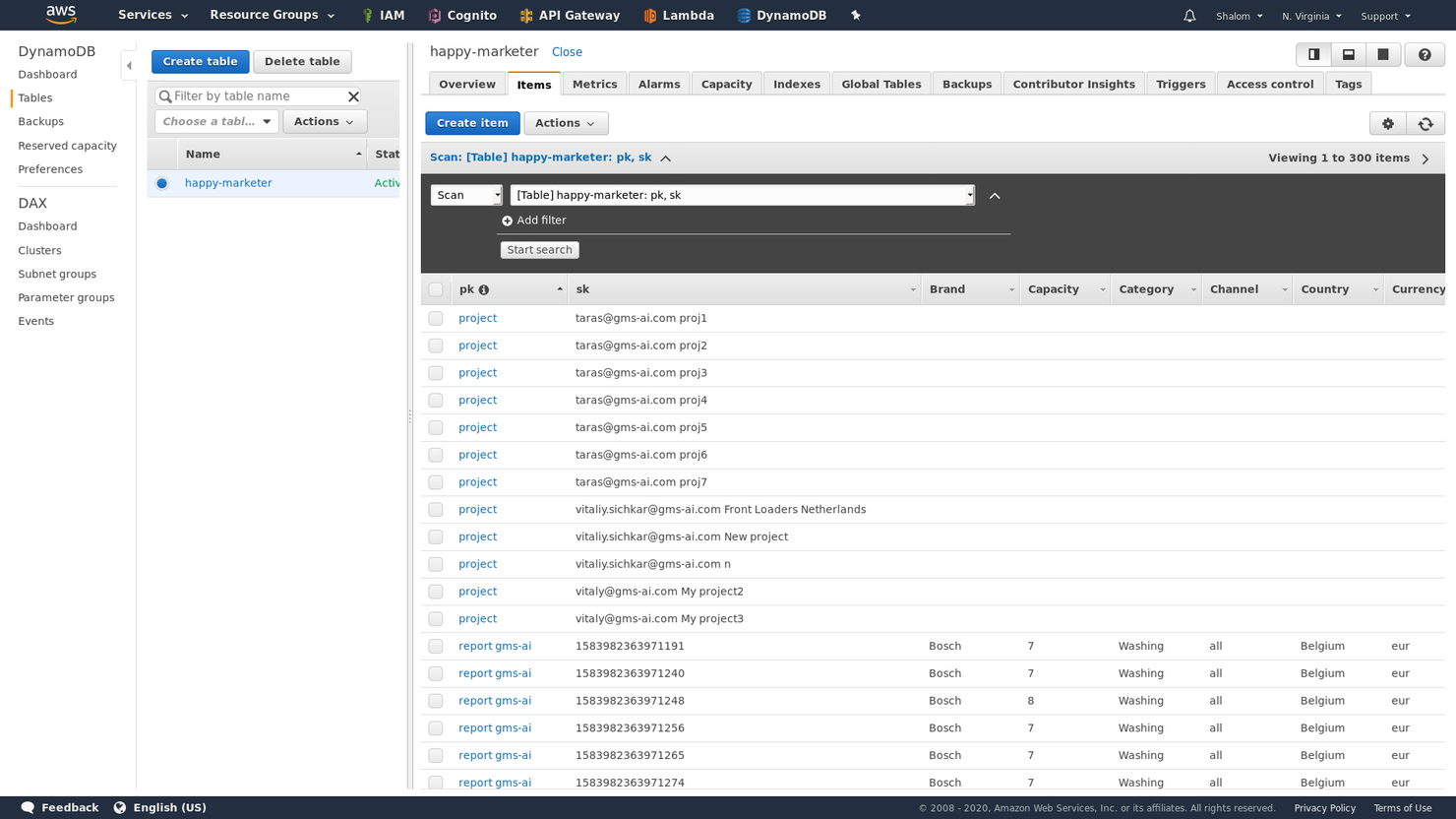
Amazon DynamoDB is a NoSQL database that supports both document and key-value data models. It is a cloud-based service that lets you store items, tables, and attributes. You can use the service on pay-as-you-go or provisioned pricing model, whichever suits your workload.
Why I Picked Amazon DynamoDB: Aside from being a fully managed NoSQL database with high availability and durability, what I like the most about Amazon DynamoDB is its Amazon Web Services (AWS) integration. This helps you do more with your data, for example, by letting you import and export from your S3 buckets. I also appreciated the ease of use, thanks to excellent documentation and a user interface that is clean and intuitive.
Amazon DynamoDB Standout Features and Integrations:
Features include on-demand and provisioned capacity modes, allowing users to optimize costs and performance based on workload requirements. It also supports global tables, enabling multi-region replication with automatic synchronization for globally distributed applications. Additionally, DynamoDB Streams provides real-time event capture, making it easy to trigger AWS Lambda functions and integrate with event-driven architectures.
Integrations include AWS Lambda, Amazon S3, Amazon Kinesis, AWS Glue, Apache Spark, Kubernetes, Grafana, and Elasticsearch.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- AWS integration to extend functionality
- Strong documentation and support
- Easy to set up and use
Cons:
- Limited to AWS cloud
- No on-premises option
Couchbase Capella is a cloud database platform, combining the speed and flexibility of a NoSQL database with the benefits of an SQL database. It also has an app development solution called Capella App Services, which you can use to design and deploy IoT, mobile, and edge applications.
Why I Picked Couchbase Capella: I chose Couchbase Capella because it is accessible to those familiar with SQL databases. It uses the SQL++ query language for operations and analytics. I like how this streamlines the move from traditional relational databases to non-relational databases, with familiar features like ACID transactions and hierarchical schemas.
Couchbase Capella Standout Features and Integrations:
Features include its built-in memory-first architecture, ensuring low-latency performance for high-speed applications. It also offers advanced mobile synchronization with Couchbase Lite and Sync Gateway, making it an excellent choice for offline-first applications. Additionally, Capella supports multi-model capabilities, allowing users to work with key-value, document, and graph data within a single database system.
Integrations include Apache Kafka, Kubernetes, Confluent Cloud, Workato, and Microsoft Azure.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Great value for money
- Built-in app development and deployment service
- Combines the benefits of SQL and NoSQL databases in one platform
Cons:
- Limited integrations
- Steep learning curve
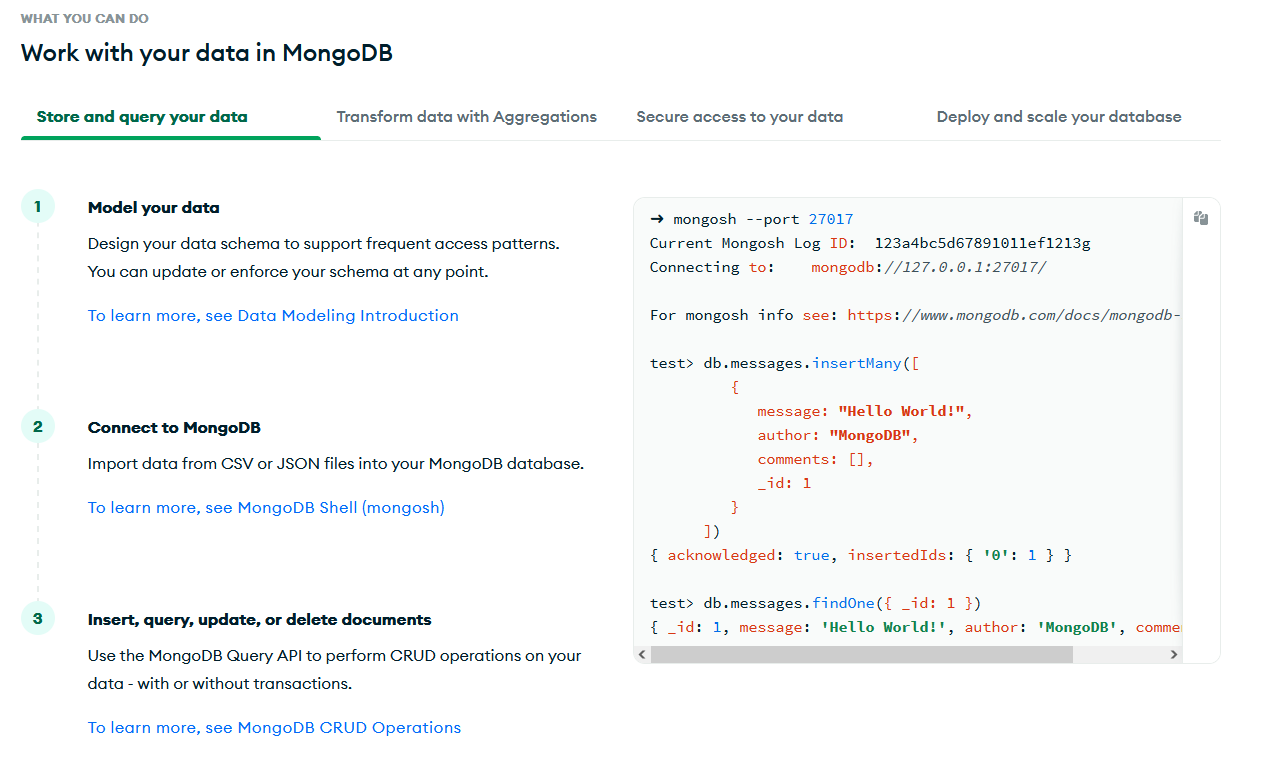
MongoDB is an open-source, document-based database. It can store structured data in the popular JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) format or in a proprietary Binary JSON (BSON) format. BSON can store more data types than JSON and encode the type and length of a piece of information, making it easier for a machine to parse (convert formatted text into a specific data structure).
Why I Picked MongoDB: I chose MongoDB because it excels at what document databases do best: providing flexible data models that can evolve as your application needs to grow. Since MongoDB scales horizontally, you can quickly add new servers to accommodate more significant amounts of data clusters, and it works well for applications that require high performance.
MongoDB Standout Features and Integrations:
Features include a flexible document-based data model, allowing developers to store and query data in a way that mirrors real-world objects. It also offers native support for sharding, enabling seamless horizontal scaling across distributed environments. Additionally, MongoDB includes an aggregation framework that simplifies complex data transformations and analytics without requiring external processing tools.
Integrations include Netlify, SAML SSO Providers, HashiCorp Terraform, and HashiCorp Fault. APIs are also available.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- No predetermined schema improves flexibility and scalability
- Comprehensive documentation and large community support
- BSON widens data type support while reducing parsing
Cons:
- Some performance issues with larger databases
- BSON uses up more storage space than JSON
Redis is an open-source, in-memory, key-value database. It delivers sub-millisecond response times, which makes it ideal for all kinds of real-time applications, such as updating the leaderboard in an online multiplayer video game or providing real-time shipping information to a customer awaiting a delivery.
Why I Picked Redis: I was impressed by Redis’ fast performance. It stores data in memory instead of on a physical disk or Solid-State Drive (SSD), so when you request data, it is unnecessary to pass through the disk, making it more efficient than many competitors.
Redis Standout Features and Integrations
Features include its in-memory data storage, which enables ultra-low latency and high-speed data retrieval, making it ideal for real-time applications. It also supports data persistence through snapshotting and append-only file (AOF) modes, allowing users to balance speed with durability. Additionally, Redis offers built-in support for pub/sub messaging, making it a strong choice for event-driven architectures and real-time notifications.
Integrations include RediSearch, RedisJSON, RedisGraph, RedisBloom, redis-cell, RedisTimeSeries, and RedisAI.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Automatic failover guarantees high availability
- Useful for real-time applications such as gaming leaderboards and analytics
- In-memory data storage delivers fast performance
Cons:
- Lack of documentation
- No Graphical User Interface (GUI)
Other NoSQL Databases
Below is a list of alternative NoSQL databases that I also recommend:
- Apache Drill
Schema-free database
- Riak
For unstructured data management
- Dgraph
For fault tolerance
- MarkLogic Server
For simplifying complex data
- DataStax Enterprise
For zero server downtime
- AstraDB
For real-time app building and scaling
- Aerospike
For reducing server and cloud footprint
- ScyllaDB
Fastest distributed database
- InterSystems Caché
For managing transactional and historical data
Related Software & Tool Reviews
If you still haven't found what you're looking for here, check out these other types of tools that we've tested and evaluated.
- Network Monitoring Software
- Server Monitoring Software
- SD-Wan Solutions
- Infrastructure Monitoring Tools
- Packet Sniffer
- Application Monitoring Tools
NoSQL Database Selection Criteria
When selecting the best NoSQL database to include in this list, I considered common buyer needs and pain points like handling unstructured or semi-structured data efficiently and scaling databases without complex infrastructure management. I also used the following framework to keep my evaluation structured and fair:
Core Functionality (25% of total score)
To be considered for inclusion in this list, each solution had to fulfill these common use cases:
- Store and retrieve unstructured or semi-structured data
- Support high availability and fault tolerance
- Scale horizontally across multiple nodes
- Handle large volumes of data with low latency
- Provide flexible schema design
Additional Standout Features (25% of total score)
To help further narrow down the competition, I also looked for unique features, such as:
- Support for multiple data models
- Built-in full-text search capabilities
- Real-time change data capture
- Integrated analytics or aggregation engine
- Edge deployment compatibility
Usability (10% of total score)
To get a sense of the usability of each system, I considered the following:
- Clear and intuitive admin interface
- Clean query language or API
- Helpful error messaging and logging
- Easy setup and configuration process
- Logical data modeling tools
Onboarding (10% of total score)
To evaluate the onboarding experience for each platform, I considered the following:
- Access to quick-start guides and tutorials
- Interactive product walkthroughs or demos
- Availability of developer documentation and SDKs
- Sample databases and pre-built templates
- Community forums or onboarding webinars
Customer Support (10% of total score)
To assess each software provider’s customer support services, I considered the following:
- Availability of 24/7 support channels
- Helpfulness and expertise of support staff
- Access to live chat or ticketing system
- Speed of issue resolution
- Availability of paid support plans
Value For Money (10% of total score)
To evaluate the value for money of each platform, I considered the following:
- Fair pricing based on storage, throughput, or usage
- Flexibility across free, standard, and enterprise tiers
- Transparent billing with no surprise fees
- Discounts for long-term or committed use
- Competitive pricing relative to performance
Customer Reviews (10% of total score)
To get a sense of overall customer satisfaction, I considered the following when reading customer reviews:
- Common pain points or recurring issues reported
- Reported reliability under production workloads
- Feedback on ease of use and learning curve
- Positive experiences with performance and speed
- Community support and knowledge sharing
How to Choose a NoSQL Database
As you're shortlisting, trialing, and selecting NoSQL databases, consider the following:
- What problem are you trying to solve - Start by identifying the NoSQL database feature gap you're trying to fill to clarify the features and functionality the tool needs to provide.
- Who will need to use it - To evaluate cost and requirements, consider who'll be using the platform and how many licenses you'll need. You'll need to evaluate if it'll just be the data team or the whole organization that will require access. When that's clear, it's worth considering if you're prioritizing ease of use for all, or speed for your technical power users.
- What other tools it needs to work with - Clarify what tools you're replacing, what tools are staying, and the tools you'll need to integrate with. This could include your existing data infrastructure, various data sources, and your overall tech stack. You might also need to decide if the tools will need to integrate together, or alternatively, if you can replace multiple tools with one consolidated NoSQL database.
- What outcomes are important - Consider the result that the tool needs to deliver to be considered a success. Think about what capability you want to gain, or what you want to improve, and how you will be measuring success. You could compare NoSQL database features until you’re blue in the face, but if you aren’t thinking about the outcomes you want to drive, you could be wasting a lot of valuable time.
- How it would work within your organization - Consider the solutions alongside your workflows and data management methodology. Evaluate what's working well, and the areas that are causing issues that need to be addressed. Remember every business is different — don’t assume that because a tool is popular that it'll work in your organization.
Trends in NoSQL Database
In my research, I sourced countless product updates, press releases, and release logs from different NoSQL database vendors. Here are some of the emerging trends I’m keeping an eye on:
- Edge-ready databases: Some NoSQL tools now support edge computing setups where data is stored and processed closer to users. It’s useful for apps with low-latency requirements or remote deployments.
- Multi-model support: More NoSQL databases are adding support for multiple data models like key-value, document, graph, and column in one system. This gives teams flexibility to run different types of workloads without switching platforms.
- Serverless architecture: Some vendors now offer serverless NoSQL databases that scale automatically and charge based on usage. It's a good option for teams that don’t want to manage infrastructure, like with Amazon DynamoDB or Azure Cosmos DB.
- Stronger consistency options: Traditionally, NoSQL prioritized availability over consistency, but now tools are offering tunable consistency levels. This helps when you need more control over how fresh or accurate your data reads are.
- Built-in full-text search: Vendors are starting to bake in search functionality so you don’t have to bolt on a separate engine like Elasticsearch. This saves setup time and keeps everything in one place.
What Are NoSQL Databases?
No Structured Query Language (SQL) databases are non-relational databases that allow for the storage, retrieval, and management of data without the need for a fixed schema. These tools are primarily used by software developers, data architects, and IT professionals who deal with large volumes of structured, semi-structured, or unstructured data.
The shift towards NoSQL databases is driven by the need to address the limitations of traditional relational databases in handling the volume, velocity, and variety of today's data. The overall value of these tools lies in their ability to provide robust, flexible, and cost-effective solutions for complex data management needs across various industries.
Features of NoSQL Databases
Here are the most important features I look for when I'm evaluating NoSQL databases:
- Scalability: This feature allows for the database to expand according to the growing data needs. The ability to scale out using distributed architecture is essential for handling vast amounts of data seamlessly, without compromising on performance.
- Flexible Data Models: NoSQL databases offer flexible data models for storing and managing diverse data types. This flexibility is crucial for accommodating the varied and dynamic nature of unstructured data without the need for predefined schemas.
- High Performance: Optimized for specific data models and access patterns, ensuring quick data retrieval and high throughput. High performance is key in scenarios where time-sensitive access to data is critical for decision-making and operational efficiency.
- High Availability: This feature ensures that the database remains accessible even in the face of hardware failures or maintenance events. High availability is critical for applications requiring constant uptime and real-time access to data.
- Data Replication: Facilitates the copying of data across multiple servers, enhancing data availability and disaster recovery. Data replication is important for maintaining data integrity and ensuring continuous access to data across geographically distributed systems.
- Partition Tolerance: The ability to continue operating despite network or partition failures. Partition tolerance is essential in distributed systems, ensuring that the system remains operational even when parts of it are not communicating effectively.
- Multi-Model Support: Supports various data models like document, key-value, graph, and column-family within a single database. Multi-model support provides the versatility to handle different types of data and access patterns, simplifying the data architecture.
- Schema-less: Allows the storage of data without a predefined schema, offering flexibility in handling changes to data structures. Schema-less databases are ideal for applications that require the ability to evolve rapidly without the need for frequent database redesigns.
- Integrated Caching: Improves performance by storing frequently accessed data in memory. Integrated caching reduces data access times significantly, enhancing the user experience and system efficiency.
- Security Features: Comprehensive security measures including encryption, access control, and auditing. Robust security features protect sensitive data from unauthorized access and breaches, which is crucial for maintaining trust and compliance.
Benefits of NoSQL Databases
NoSQL databases offer a flexible, scalable, and efficient way to manage data, making them an attractive option for organizations and developers dealing with large volumes of diverse data types. Unlike traditional relational databases, NoSQL databases are designed to handle unstructured and semi-structured data, offering unique advantages that can significantly enhance business operations and data management strategies. Here are five primary benefits of NoSQL databases for users and organizations:
- Scalability: Easily manage data growth with distributed architecture. NoSQL databases are inherently designed to scale out across multiple servers and data centers, allowing businesses to handle increasing volumes of data without a hitch, supporting growth and ensuring performance is maintained.
- Flexibility: Adapt to changing data models without downtime. The schema-less nature of NoSQL databases allows for the storage of unstructured and semi-structured data, providing the flexibility to rapidly evolve your application without the need to modify a rigid database schema, thus accelerating development cycles.
- High Performance: Achieve faster data access and processing. NoSQL databases can provide superior performance for certain types of operations, including those involving large volumes of data and real-time applications, by leveraging optimized storage, caching, and retrieval mechanisms tailored to specific data models.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduce costs with efficient data storage and processing. The distributed nature of NoSQL databases, combined with their ability to efficiently manage large volumes of diverse data, can lead to significant cost savings in hardware, storage, and maintenance compared to traditional database systems.
- Data Variety Handling: Store and query a wide range of data types. NoSQL databases support multiple data models, including key-value, document, wide-column, and graph formats, enabling organizations to leverage a single database for a variety of data types and applications, simplifying data management and enhancing analytical capabilities.
Costs & Pricing For NoSQL Databases
NoSQL databases offer a variety of plan and pricing options designed to accommodate the needs of businesses of all sizes, from startups to large enterprises. These databases are tailored to manage large volumes of structured and unstructured data efficiently, offering scalability, flexibility, and high performance.
The pricing models vary significantly among different NoSQL database providers, typically based on factors such as data storage, read/write throughput, number of transactions, and level of support required.
Plan Comparison Table For NoSQL Databases
Here's a summary overview of the different pricing plans and cost ranges typically available for these tools:
| Plan Type | Average Price | Common Features |
|---|---|---|
| Free | $0 | Basic access, limited storage and throughput, community support |
| Standard | $100 - $1,000/month | Increased storage and throughput, technical support, basic security |
| Professional | $1,000 - $10,000/month | Enhanced security features, higher throughput and storage limits, 24/7 support |
| Enterprise | Custom pricing | Customized solutions, dedicated support, unlimited storage and throughput |
NoSQL Database FAQs
Here are the most common questions that people ask when searching for information on NoSQL databases.
What is the difference between SQL and NoSQL?
SQL databases use defined tables, rows, and columns to store data, while NoSQL databases are unrestricted by the same framework.
What are NoSQL databases mainly used for?
NoSQL databases are used to collect and process structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data that a relational database typically cannot handle.
Is NoSQL faster than SQL?
Choosing the right NoSQL database can significantly streamline data management, scalability, and performance while boosting flexibility and efficiency—whether you’re handling large-scale web applications, real-time analytics, or IoT data processing. However, the sheer number of available NoSQL database solutions—combined with the challenge of navigating different data models, scaling complexities, and integration concerns—can make selecting the best option overwhelming.
In this article, I leverage my years of experience in database management and testing dozens of NoSQL solutions to break down what these databases offer, who they’re best suited for, and how they can help you optimize performance, improve data accessibility, and scale seamlessly.
Because NoSQL databases are used for very specific instances, they are typically faster at achieving those instances than a traditional SQL database.
Choose the Right NoSQL Database
There’s a large opportunity for efficiency gains if you select better database tools that make it easier for your organization to collect and process large amounts of unstructured data.
This is why it’s important you understand what NoSQL databases are and their varying uses. Hopefully, this article will help you make the right choice for your organization.
Subscribe to the CTO Club newsletter to get the latest articles and insights on SaaS technology.