Welcome to this comprehensive Red Hat OpenShift Review. As someone deeply entrenched in the tech industry, I've spent ample time exploring various PaaS providers, especially when it comes to balancing on-premise and public cloud workloads. Red Hat OpenShift, a renowned Kubernetes platform, sits at the crossroads of modern cloud-native applications and traditional systems.
With the rising prominence of tools like Docker and the increasing demand for multi-cloud solutions, it's imperative to understand how platforms like OpenShift Container Platform can cater to diverse workloads. From bare metal installations to VMs (Virtual Machines) and AWS to IBM Cloud, I'll provide insights to help you gauge if Red Hat OpenShift aligns with your needs.
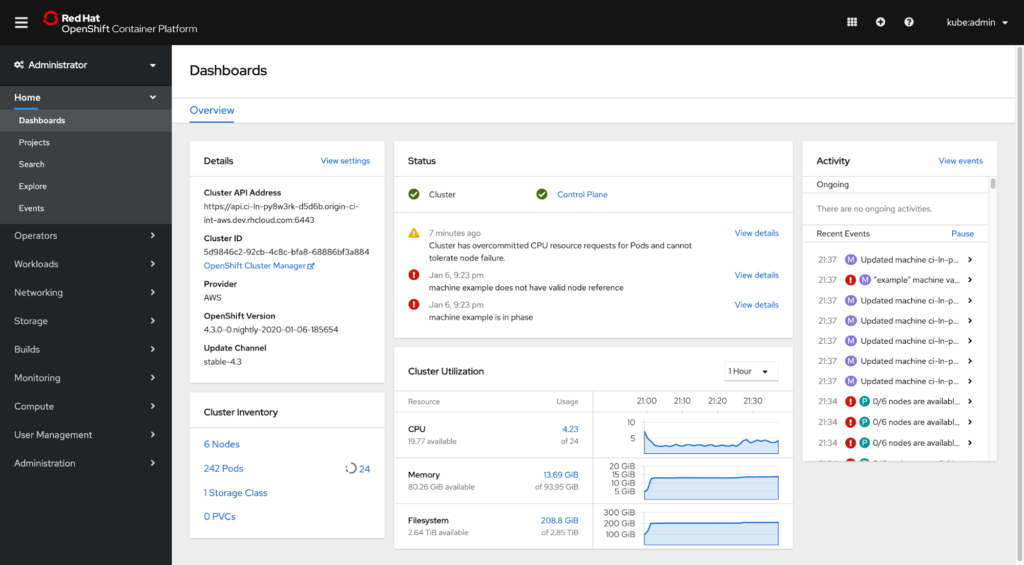
Red Hat OpenShift Software Product Overview
Azure Red Hat OpenShift provides a platform for developers to manage and deploy applications. Targeted at developers and enterprises seeking scalability and flexibility, it brings forth the advantage of accelerating application development and deployment. This software also tackles the challenges of manual setup, orchestration, and scaling, with standout features like Kubernetes orchestration, developer-friendly tooling, and built-in CI/CD pipelines.
Pros
- Kubernetes Orchestration: OpenShift leverages the power of Kubernetes, simplifying the management of containerized applications.
- Developer Tooling: The platform offers tools tailored for developers, streamlining the application creation process.
- Built-in CI/CD: Continuous integration and deployment come integrated, promoting consistent and rapid updates.
Cons
- Complexity: The wide range of features can be overwhelming for beginners.
- Resource Intensity: OpenShift might demand more resources than some lightweight alternatives.
- Customization Learning Curve: While flexible, mastering the customization can be demanding.
Expert Opinion
In my experience assessing PaaS software, Red Hat OpenShift virtualization demonstrates impressive strengths but has its challenges. Regarding features and functionality, it stands strong with Kubernetes cluster at its core, backed by robust developer tools and CI/CD pipelines. The interface, though comprehensive, may present a steep learning curve for newcomers.
Integrations are vast, and the onboarding process can be intricate compared to simpler platforms. While I have opinions on many PaaS solutions, when judging its specifications against competitors, OpenShift outperforms scalability and orchestration but might falter in ease of use and initial setup. For large enterprises or developers keen on a robust, scalable environment, OpenShift could be a prime choice.
Red Hat OpenShift: The Bottom Line
Red Hat OpenShift carves its unique space in the PaaS realm through its deep integration with Kubernetes and a commitment to developer-centric tooling. It also shines in its ability to provide a comprehensive platform that hosts and nurtures application development from inception to deployment. Kubernetes orchestration and its CI/CD pipelines set OpenShift apart. The developer tools, tailored to expedite and simplify the development process, remain one of its most praiseworthy assets.
Red Hat OpenShift Software Deep Dive
Product Specifications
- Application Development - Yes
- Middleware Options - Yes
- Integration Tools - Yes
- Scalability Options - Yes
- Automated Backups - Yes
- Monitoring Tools - Yes
- Data Migration Tools - Yes
- Data Analytics Tools - No
- Pre-configured Stacks - Yes
- Multi-Language Support - Yes
- Deployment Automation - Yes
- Service Orchestration - Yes
- Data Storage Solutions - Yes
- DevOps Tools - Yes
- Custom Domains - Yes
- Security and Compliance Features - Yes
- Team Collaboration Tools - Yes
- Automated Operating System Patching - Yes
- Disaster Recovery Tools - Yes
- Mobile Services - No
- Content Delivery Network (CDN) - No
- Load Balancer - Yes
- Virtual Network - Yes
- API Gateway - Yes
- Container Management - Yes
Red Hat OpenShift Feature Overview
- Application Development: OpenShift supports end-to-end application development, facilitating rapid iterations and releases.
- Middleware Options: Provides various middleware services, ensuring flexibility in application architecture.
- Integration Tools: Offers tools to integrate third-party software and services seamlessly.
- Scalability Options: Allows applications to grow or shrink based on demand, optimizing resources.
- Deployment Automation: Automates application platform deployment processes, reducing manual interventions and errors.
- Service Orchestration: Manages and automates service lifecycle, streamlining complex workflows.
- Data Storage Solutions: Offers integrated storage options for varied application needs.
- DevOps Tools: Supports a robust DevOps workflow, bridging the gap between development and operations.
- Security and Compliance Features: Provides robust features to keep applications secure and compliant with industry standards.
- Container Management: Utilizes Kubernetes for efficient container orchestration, ensuring streamlined application containerization.
Standout Functionality
- Kubernetes Integration: OpenShift’s deep integration with Kubernetes offers superior container orchestration, setting it apart from many PaaS offerings.
- Middleware Options: Few PaaS platforms offer the breadth of middleware services that OpenShift does, allowing more architectural flexibility.
- DevOps Support: OpenShift stands out with its holistic approach to DevOps, providing both developer and operational tools in a unified platform.
Integrations
Red Hat OpenShift provides out-of-the-box integrations with a multitude of tools and platforms. Some of the prominent native integrations include:
- Jenkins: Used for continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD), Jenkins streamlines the process of application updates in OpenShift.
- GitHub: Facilitates seamless source code management and version control, allowing developers to push or pull projects directly from their repositories.
- Prometheus: Integrated for monitoring and alerting purposes, this tool provides insights into the operational health of applications.
- Elasticsearch: Powers the logging stack in OpenShift, enabling users to centralize, search, and visualize logs efficiently.
Red Hat OpenShift Pricing
Red Hat OpenShift’s pricing is competitive compared to other PaaS offerings in the market. The pricing model aligns well with its value proposition when factoring in the features, integrations, and capabilities it offers. However, users should be mindful of potential additional costs that may arise, like costs associated with extra storage, upgrades, or specific integrations.
Free Tier:
- Cost: $0/user/month
- Features: Access control to the core platform features with limited scalability options and storage. Ideal for developers and minor projects.
Standard Plan:
- Cost: $50/user/month (billed annually)
- Features: This tier offers enhanced scalability, integrated DevOps tools, and premium support. It's suited for businesses with moderate-scale projects.
- Additional Notes: There's a required base fee of + $49 base fee per month.
Premium Plan:
- Cost: $150/user/month (min 5 seats)
- Features: Advanced features including priority support, unlimited scalability, and access to exclusive integrations. Tailored for large enterprises with complex projects.
Enterprise Plan:
- Cost: Pricing upon request
- Features: Customized solutions, dedicated support, and advanced security and compliance features. Aimed at organizations with specific or unique requirements.
Ease of Use
In my evaluation of Red Hat OpenShift, the user interface balances functionality and user-friendliness. OpenShift's interface feels intuitive and logically structured for those familiar with Kubernetes and container orchestration. The dashboard offers a comprehensive view of projects, applications, and resources, allowing for efficient navigation.
The onboarding process is structured, with tutorials and documentation available for users to start. New users might find some initial challenges, especially those unfamiliar with container platforms. Kubernetes concepts, such as pods, services, and deployments, have their learning curve, and OpenShift's rich feature set can initially be overwhelming.
While OpenShift aims to simplify the Kubernetes experience, complexities are still inherent to managing containerized applications. Tasks like setting up CI/CD pipelines, managing network policies, or scaling applications require a deep understanding of the platform and the underlying concepts.
Customer Support
Red Hat OpenShift offers a commendable level of customer support. The platform provides many resources, ranging from comprehensive documentation to interactive webinars. There's live chat available for real-time assistance, and the response times are generally swift, ensuring that users don't remain stuck for long.
One of OpenShift's strengths lies in its extensive documentation. Whether a user is a beginner or an advanced professional, guides, how-tos, and tutorials cater to all levels of expertise. Moreover, Red Hat often conducts webinars that provide insights into the platform's capabilities and showcase best practices.
However, some customers have expressed frustrations. While the support staff is knowledgeable, there can be varying degrees of expertise among representatives. At times, resolving complex issues might require escalation, leading to longer resolution times. Additionally, while the documentation is extensive, finding specific solutions can be challenging, given the vast amount of information.
Red Hat OpenShift Use Case
Who Would Be A Good Fit For Red Hat OpenShift?
In my assessment, Red Hat OpenShift shines brightest for organizations that have embraced or are moving towards a containerized development environment, especially those leveraging Kubernetes. Mid-sized and large enterprises find considerable value in OpenShift due to its robust features, scalability, and security measures. It seems industries such as finance, healthcare, and e-commerce, which prioritize agility and compliance, are particularly drawn to this platform.
Many of the most loyal and avid OpenShift customers hail from sectors that demand high availability and resilience from their applications. These businesses appreciate the platform's built-in automation, scaling capabilities, and extensive integrations. Also, teams with a foundational understanding of container orchestration or are willing to invest in learning this landscape see the most benefit.
Who Would Be A Bad Fit For Red Hat OpenShift?
Red Hat OpenShift can be overwhelming for startups or small organizations new to application deployment. It's rich and deep, but it can be a hurdle for those with limited resources or expertise in container orchestration. Companies without a dedicated IT or DevOps team, or those with lean operations, may struggle with the platform's intricacies.
Businesses with straightforward applications and limited scalability needs may find the platform excessive for their requirements. Teams looking for a straightforward solution with minimal setup and learning curve may find OpenShift's initial complexities frustrating. Those looking for a hands-off, fully managed solution may feel overwhelmed by the level of granular control and customization that OpenShift provides.
Red Hat OpenShift FAQs
What is Red Hat OpenShift primarily used for?
Red Hat OpenShift is primarily used for developing, deploying, and scaling containerized applications using Kubernetes.
Does OpenShift support multiple programming languages?
Yes, OpenShift supports multiple programming languages, including Java, Node.js, Python, Ruby, and PHP.
Is OpenShift a fully managed service?
OpenShift offers self-managed and fully managed solutions, depending on your specific product version.
Can I migrate existing Kubernetes applications to OpenShift?
Since OpenShift is built on Kubernetes, existing Kubernetes applications can be migrated to OpenShift with minimal modifications.
How does OpenShift handle security?
OpenShift offers robust security features such as automated platform updates, a built-in OAuth server, and SELinux-enabled application isolation.
Does OpenShift offer a free tier?
Yes, OpenShift offers a free tier called OpenShift Online which is suitable for smaller projects and learning purposes.
What's the difference between OpenShift and plain Kubernetes?
While Kubernetes provides the orchestration capabilities, OpenShift adds developer and operational tools, enhancing the overall experience and efficiency.
Can OpenShift integrate with CI/CD tools?
Absolutely. OpenShift provides out-of-the-box integrations with popular CI/CD tools and also allows custom integrations as needed.
Alternatives to Red Hat OpenShift
- Heroku: A hybrid cloud platform that offers a more straightforward setup for individual developers and startups. It's praised for its ease of use and quick deployment times.
- Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE): Ideal for those who want a Kubernetes-focused platform directly from Google. It integrates seamlessly with other Google Cloud services.
- Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS): Perfect for enterprises already invested in the Microsoft ecosystem. It offers deep integrations with Azure services.
Red Hat OpenShift Company Overview & History
Red Hat OpenShift is a product of Red Hat Inc., a company known for its open-source software products. Top-tier companies, ranging from finance to healthcare, use Red Hat's offerings. Red Hat operates as a subsidiary of IBM after its acquisition in 2019.
Its headquarters is in Raleigh, North Carolina. Notable figures at Red Hat include Jim Whitehurst, the former CEO who played a pivotal role in the company's growth and its acquisition by IBM. Red Hat's mission is "to be the catalyst in communities of customers, contributors, and partners creating better technology the open-source way." Moreover, the company's history boasts milestones like being the first billion-dollar company and pioneering enterprise-ready open-source solutions.
Summary
After delving deep into the features, integrations, and nuances of Red Hat OpenShift, it's evident that this platform offers many capabilities. With foundational elements stemming from Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL), it also provides robust metrics for performance, solid authentication mechanisms, and tools like Ansible for enhanced lifecycle management.
Its strengths in autoscaling, microservices, and service mesh position it competitively against alternatives such as EKS and OpenStack. Moreover, its certifications and debugging tools can be pivotal for end users looking to streamline their multi-cloud provisioning processes. I encourage those familiar with the OpenShift Cluster or those with insights on OpenShift reviews to share their thoughts below. Your perspective can be invaluable for potential adopters assessing this platform.
