Unlocking Innovation: Low code tools enable rapid app development, modernization of legacy systems, and alignment with business strategy for greater ROI.
Democratizing Development: Low code is no longer just for developers; it empowers business analysts and non-technical stakeholders to contribute to app development and business growth.
Rising Popularity of Low Code: Increasing adoption of low-code tools by developers, boosting productivity, streamlining design-to-code processes, and fostering innovation.
Driving Organizational Change: Low code empowers Enterprise Architects and C-level executives to introduce new thinking, drive innovation, and create new revenue streams.
Benefits of Low Code: Low code streamlines development, optimizes processes, accelerates time-to-market, and ensures alignment with business goals for enhanced productivity.
Are you struggling to keep pace with rapidly changing business needs due to legacy systems and limited resources? This comprehensive guide will show you how low-code platforms are transforming enterprise architecture and helping organizations achieve greater agility, innovation, and competitive advantage.
The Enterprise Architect's Dilemma
Imagine this: Your team is preparing for a major product launch when a key customer requests a critical feature change. Due to your monolithic architecture, your developers estimate it will take weeks to implement. Meanwhile, your competitors are releasing new features weekly using low-code platforms for building applications.
You're faced with a familiar dilemma – push back the launch date yet again or disappoint an important customer.
This all-too-common scenario raises the question:
What happens when inflexible, outdated systems hinder innovation and agility? Or when you struggle to align your organization's tech strategy with business goals and teams' resources?
There are two possible outcomes:
(1) You continue with traditional development.
This ultimately leads to slow, costly, and rigid processes. While this approach avoids the learning curve of new tools, adapting to changing business needs is more challenging due to legacy system constraints and the inability to optimize time and costs.
(2) You can embark on a digital transformation journey leveraging low code.
This will enable rapid app development and deployment and help you tackle some of enterprise architects' most significant challenges.
For example, with low-code platforms, you can:
- Modernize legacy systems to build future-proof and secure apps
- Ensure the company is up to date with current tech trends
- Accelerate time-to-market through automation
- Manage skill gaps
- Standardize and ensure everything aligns with the business strategy to increase ROI.
These are among the challenges that low-code platforms effectively address and resolve for enterprise architects.
Understanding Low-Code Development
What Is Low-Code?
In practice, low code streamlines everything from design to code and from an idea to an app. These tools contain all the capabilities developers need to craft custom software solutions.
Before continuing, to maximize low-code and no-code potential, you need to understand the idea behind low-code tools, even if you're not a developer using them to build apps. Until very recently, low-code was perceived as a technology for developers only.
However, low-code tools enable a broader range of users, including business analysts and other non-technical stakeholders, to contribute to app development and business growth.
For example, enterprise architects and C-level executives use low code to improve software quality, foster innovation and introduce new thinking within their organizations.
This approach allows for improvement and creates new revenue streams, a win-win situation for all involved.
Key Features of Low-Code Platforms
A typical low-code development platform includes one or more of the following features:
- Visual IDE: Defines the UIs, workflows, and data models of your application and, where necessary, adds hand-written code.
- Connectors: Automatically handle data structures, storage, and retrieval across various back-ends or services.
- Automated tools: Build, debug, deploy, and maintain the application in the testing, staging, and production stages.
- Design-to-code capabilities: Provides designers and developers a platform to design prototypes and transform designs into clean, production-ready code.
- Collaboration tools: Allow multiple users to work simultaneously, track progress, share code, etc.
The Growing Adoption of Low-Code
Since no-code platforms and low-code development is gaining momentum, more organizations are turning to it.
A 2024 Reveal survey found that:
- Over two-thirds (71.8%) of developers use low-code or no-code app builders
- More than half (56.4%) anticipate more significant reliance on these tools
- Nearly all respondents (90.4%) said that low-code tools boosted developer productivity in their organizations
As mentioned, until very recently, low-code was perceived as a technology for developers only.
However, low-code tools enable a broader range of users, including business analysts and other non-technical stakeholders, to contribute to app development and business growth and improve time to market.
Since low-code development is gaining momentum, more organizations are turning to it.
Future-Proofing Old Infrastructures
That said, building future-proof and secure apps and accelerating time-to-market depend on the tools. Organizations with outdated infrastructures have hindered abilities to innovate and compete effectively.
Can the rip-and-replace scenario work 100% in that situation? Not entirely, because you can’t simply eliminate traditional development.
While low-code platforms are great for rapid prototyping and small to medium-sized applications, they might not scale as efficiently as traditionally coded solutions for large enterprises with specific use cases and extensive needs.
Outdated systems are often heavy and bloated and lack essential modern tools like Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) or version control systems. This overall complexity poses challenges, particularly to tech newbies.
By integrating low-code tools as a solution, you will:
- Streamline processes
- Improve collaboration
- Keep up with current development trends
- Empower developers to build apps without having to write code line by line
Automated Precision for Faster Time to Market
Competition puts pressure on companies, and product and service delivery speed can be pivotal to success or failure. More and more C-level executives are implementing low-code solutions to address this challenge head-on.
This approach reduces strain on IT resources and ensures timely product delivery, as low-code tools can replace manual and error-prone hand coding.
Interestingly, certain products have simplified WYSIWYG drag-and-drop interfaces, and their code generation capabilities provide complete control.
In turn, digital product, design, and development teams can deliver pixel-perfect applications up to 80% faster while increasing customer satisfaction by as much as 35%.
Further, this streamlined approach also leads to better ROI because:
- It aligns development efforts with business goals
- It enhances customer satisfaction by delivering high-quality, standardized code that ensures consistency and reusability across projects
From Deficit to Proficiency: Managing the Skill Gap
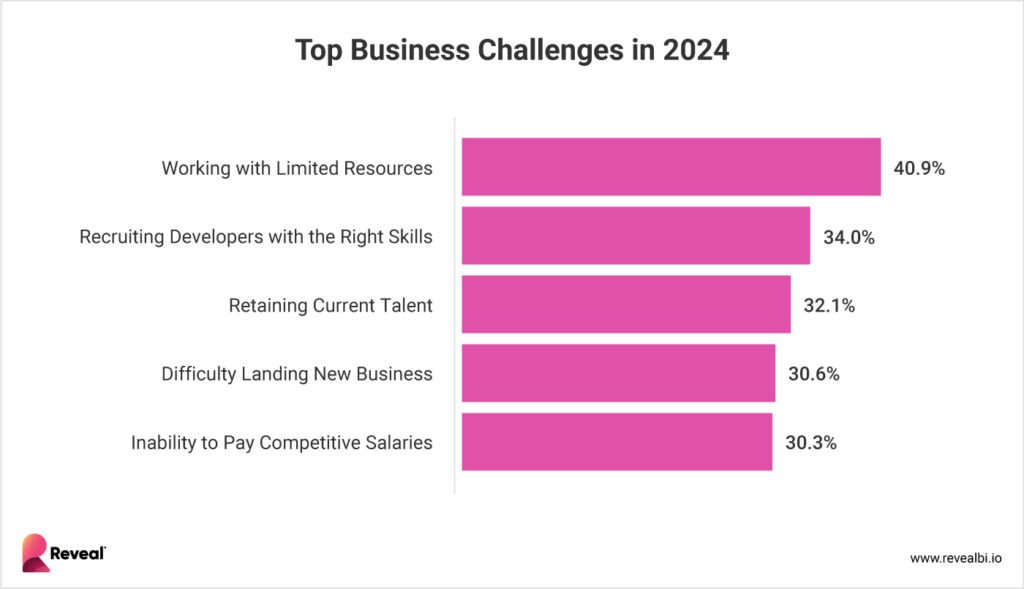
A Reveal Survey Report found that “the biggest business challenge for the technology industry is working with limited resources (40.9%),” which is why more business owners are incorporating low-code solutions.
Such tools are also a huge time saver in teams that do not collaborate or include designers. More advanced solutions typically have an integrated design system and the ability to instantly convert design files to pixel-perfect code.
Adopting low-code platforms enables rapid application development and deployment, which allows you to focus strategically on maximizing your team's resources and skills.
These tools allow citizen developers and less experienced programmers to handle basic tasks and app functionality. This will enable engineers to refocus their efforts on business logic and more complex app scenarios.
Comparison with No-Code Platforms
While often mentioned together, low-code and no-code platforms serve distinctly different purposes in the enterprise architecture landscape. Understanding these differences is essential for making informed technology decisions.
Customization Capabilities
Low-code platforms offer significantly greater flexibility than their no-code counterparts. With low code, professional developers can extend applications by adding custom code when needed, enabling complex integrations and specialized functionality that pre-built components can't provide.
In contrast, no-code platforms apply constraints to the development environment, limiting users' ability to extend applications beyond the vendor's supplied solution.
This trade-off simplifies the user experience but can create limitations for complex enterprise requirements.
Developer Spectrum
As you may expect, low-code platforms support a broader spectrum of users:
- Citizen developers can quickly build productivity applications or initiate UI development for enterprise applications
- Business analysts can create workflow solutions without deep technical knowledge
- Professional developers can develop enterprise-grade applications, REST APIs, and microservices while maintaining control over the architecture
No-code tools primarily target business users and citizen developers with limited or no programming experience. They offer simplified interfaces but more restricted output.
Technical Depth and Extensibility
Professional developers using low-code platforms can encapsulate their code into shareable, reusable modules when custom functionality is necessary. These modules become drag-and-drop components for the entire development team, combining the speed of visual development with the power of custom code.
This capability creates a significant advantage for enterprise architects facing complex system integration challenges or unique business requirements that off-the-shelf solutions can't address.
Resource Requirements
While no-code platforms typically require minimal technical expertise, they often demand more post-deployment customization when business needs evolve. Low-code solutions require some technical knowledge but provide greater long-term flexibility and reduced technical debt.
For enterprise architects balancing rapid development with future-proofing concerns, low-code platforms often represent the optimal middle ground between traditional development's flexibility and no-code's accessibility.
Low-Code Security and Compliance
As low-code platforms increasingly become part of enterprise architecture, security and compliance considerations take center stage. While these platforms offer rapid development benefits, they also introduce unique security challenges that must be addressed.
Balancing Speed with Security
The accelerated development pace that makes low-code platforms attractive can potentially create security blind spots. When applications are built rapidly, traditional security review processes might be compressed or overlooked, creating vulnerabilities.
Common security concerns include:
- Insufficient testing of auto-generated code
- Incomplete access control implementation
- Inadequate data validation
- Potential for shadow IT development outside governance frameworks
For enterprise architects, this means establishing clear security protocols tailored to low-code development environments, where the traditional "slow and thorough" security review process must adapt to faster development cycles.
Compliance in Regulated Industries
Organizations in heavily regulated industries like healthcare, finance, and government face additional challenges when adopting low-code platforms. These industries must ensure that any application—regardless of how quickly it's developed—meets strict compliance requirements.
Key compliance considerations include:
- Data residency and sovereignty requirements
- Audit trails for all development activities
- Role-based access controls
- Documentation of security measures
Many enterprise architects find that leading low-code platforms now offer pre-built compliance templates and certification frameworks that significantly reduce the burden of meeting these requirements.
Security Innovations Through Low-Code
Interestingly, low-code platforms are also driving security innovations. By centralizing application development on a governed platform, organizations can enhance their security posture compared to traditional development approaches.
These platforms can:
- Enforce consistent security patterns across all applications
- Implement organization-wide security updates simultaneously
- Provide visibility into all applications accessing enterprise data
- Create secure data workflows with pre-validated components
For enterprise architects, this represents an opportunity to establish security-by-design principles baked into the low-code platform itself rather than applied as an afterthought to individual applications.
Best Practices for Secure Low-Code Development
To maximize security in low-code environments, forward-thinking organizations are implementing specific governance frameworks:
- Centralized management of low-code platform security settings
- Regular security assessments of the platform and its components
- Clear separation between development, testing, and production environments
- Integration with existing enterprise security monitoring tools
- Training for citizen developers focused specifically on security awareness
By implementing these practices, enterprise architects can help their organizations realize the speed benefits of low-code platforms while maintaining robust security and compliance standards.
Low-Code App Lifecycle Management
For enterprise architects, the actual value of low-code platforms such as Outsystems low-code platform extends far beyond rapid application development. These platforms provide comprehensive support across the entire application lifecycle, transforming how organizations approach development, testing, deployment, and maintenance.
End-to-End Lifecycle Support
Modern low-code platforms have evolved to include integrated tools and services that support every phase of the application lifecycle:
- Ideation and requirements gathering
- Development and customization
- Testing and quality assurance
- Deployment across multiple environments
- Monitoring and performance management
- Continuous improvement and iteration
This comprehensive approach means enterprise architects no longer need to stitch together disparate tools to manage the application lifecycle, reducing integration challenges and streamlining governance.
Embracing Agile and DevOps
Low-code platforms have increasingly incorporated core Agile and DevOps principles into their foundations, enabling organizations to implement these methodologies more effectively:
- Iterative development through sprint-based planning tools
- Continuous integration through automated testing
- Continuous deployment through one-click deployment options
- Feedback loops through integrated monitoring and analytics
For enterprise architects, this built-in support for Agile and DevOps practices means teams can focus on delivering business value rather than managing development processes and infrastructure.
Collaborative Workflows
One of the most significant advantages of low-code platforms in application lifecycle management is their ability to facilitate collaboration between different stakeholders:
- Business analysts can define requirements directly in the platform
- Developers can implement functionality using visual tools
- QA teams can create and execute tests within the same environment
- Operations teams can monitor deployed applications through integrated dashboards
This collaborative approach breaks down traditional silos between business and IT, enabling truly cross-functional teams to work together throughout the application lifecycle.
Governance and Control
Despite the increased speed and flexibility that low-code platforms provide, they also offer robust governance capabilities that are essential for enterprise architects:
- Version control and audit trails for all changes
- Role-based access controls for different team members
- Environment management for development, testing, and production
- Automated quality checks and code reviews
These governance features ensure the accelerated development pace doesn't compromise quality, security, or compliance.
Metrics and Continuous Improvement
Leading low-code platforms now include sophisticated analytics capabilities that help enterprise architects measure and improve application lifecycle processes:
- Development velocity metrics
- Quality and testing coverage
- Deployment frequency and success rates
- Application performance and user satisfaction
By leveraging these metrics, organizations can continuously refine their application lifecycle processes, identify bottlenecks, and implement improvements that further accelerate delivery while maintaining quality.
Low-Code: Leading the Change in App Development
Low-code software redefines how businesses approach application development, collaboration, and business growth initiatives. Low-code software equips organizations with the tools to adapt to changing market demands by simplifying and accelerating development.
This transformative technology reduces time to market and enhances both operational efficiency and ROI by streamlining workflows and ensuring alignment with business goals.
What’s Next?
Subscribe to our newsletter for the latest insights from CTOs and aspiring tech leaders.
We'll help you scale smarter and lead stronger with guides, resources, and strategies from top experts!








